D. The United States 1919 - 1941
 At the end of the First World War, the United States was the richest country on earth. During the 1920s it experienced a 'boom' of industrial growth which led to President Hoover saying in 1929: We have more cars, more bathtubs, oil furnaces, silk stockings, bank accounts than any other people on Earth... I have no fears for the future of our country. It is bright with hope'. However, the US economy was not as healthy as this speech indicated and not all Americans shared in this wealth. Indeed the Wall Street Crash of 1929 led to an economic catastrophe - the Great Depression.
At the end of the First World War, the United States was the richest country on earth. During the 1920s it experienced a 'boom' of industrial growth which led to President Hoover saying in 1929: We have more cars, more bathtubs, oil furnaces, silk stockings, bank accounts than any other people on Earth... I have no fears for the future of our country. It is bright with hope'. However, the US economy was not as healthy as this speech indicated and not all Americans shared in this wealth. Indeed the Wall Street Crash of 1929 led to an economic catastrophe - the Great Depression.
In this unit you will study life before the Wall Street Crash, the reasons and impact of the Great Depression, and how President Roosevelt attempted to save America through his New Deal policies.
 The USA was established on 4 July 1774 when thirteen British colonies in North America (shown here in red) declared that they wanted to be independent from Britain. After defeating Britain in the American War of Independence, the Americans joined the thirteen colonies together into a new nation - the United States of America.
The USA was established on 4 July 1774 when thirteen British colonies in North America (shown here in red) declared that they wanted to be independent from Britain. After defeating Britain in the American War of Independence, the Americans joined the thirteen colonies together into a new nation - the United States of America.
The thirteen states were eventually joined by many others; now there are 50 states represented by the 50 stars on the flag.
Before studying this topic, it is very useful if you can understand how the US constitution works.
Watch this video on the US government.
- Note down key features of the government
- What does each branch of the government do?
Soon after winning independence, the Americans drew up a Constitution ![]() . Part of the constitution was the Bill of Rights which sets out the rights of the people.
. Part of the constitution was the Bill of Rights which sets out the rights of the people.

The constitution describes a federal system of government. This means that the job of running the country is divided between two kinds of government - the central, or federal, government in Washington, and the local governments of each of the 50 states.
As you will have seen from the video above, there are three 'branches' of government:
- The legislative branch called Congress, makes the country's laws
- The executive branch, The President, carries out these laws
- The Judicial branch makes sure that the laws are obeyed
Nobody can belong to more than one of these branches. The system is meant to create 'checks and balances' to prevent any one branch becoming too powerful.
Americans vote in elections for the President and for Congress. They also vote in local elections for their state governors and state legislatures
In pairs study the diagram below. Give examples of how one branch of government can prevent another branch becoming too powerful.
Can you think of any examples where this has operated in practice in US politics in recent years?
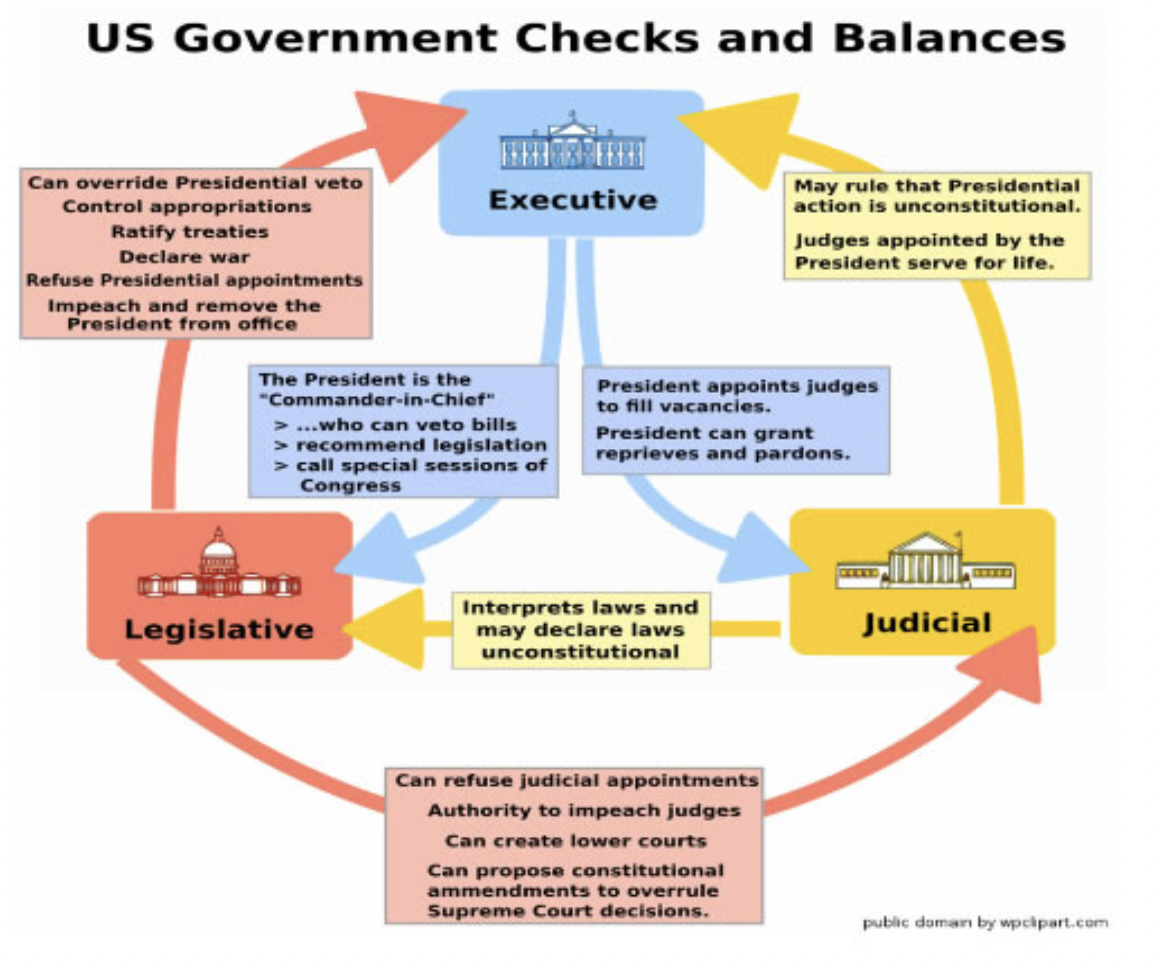
Add the correct word into the gaps
checks and balances federal executive Bill of Rights Constitution legislative Judicary Congress
The US has a system of government in which the fifty state governments share power with the central government in Washington. The sets out the rules by which America is government and the sets out the rights that people have. The branch of the government is called and this makes the laws. The branch of government is the President who ensures that the laws are carried out. The makes sure that laws are obeyed. The system of govenrment operates via so that each branch of government is prevented from becoming too powerful.
The US has a federal system of government in which the fifty state governments share power with the central government in Washington. The consitution sets out the rules by which America is government and the Bill of Rights sets out the rights that people have. The legislative branch of the government is called Congress and this makes the laws. The executive branch of government is the President who ensures that the laws are carried out. The Judiciary makes sure that laws are obeyed. The system of govenrment operates via checks and balances so that each branch of government is prevented from becoming too powerful.
The first part of this study uses a lot of economic terminology so before you carry on check you understand the meaning of the terms below.
Discuss in pairs the meaning of these economic terms. Look up any terms that you are unsure of.
- Supply and demand
- Overproduction
- Speculation
- Protectionism
- Mixed economy
- Tariffs
- Market economy
- Capitalism
- Economic depression
- Credit
- Economic recession
- Trade Union
- Corporation
Constitution: a set of rules on how a country should be run
Veto: the right to reject a decision or proposal
Bill of Rights: Document setting out the rights of the American people e.g. the right to free speech
Rugged individualism: the belief that individuals should fend for themselves without the help of federal government and that such help would only weaken the ideals of independence and self-worth
Now move on to these sections of this Depth Study:

